About Venture Philanthropy: Social Investment Partners
About Venture Philanthropy
In Europe and the US, theories and methodologies such as venture capital or private equity investment have been implemented to provide support to social purpose organizations. This venture philanthropy methodology has been established by successful entrepreneurs/investors and foundations as a support providing organization, that not only serves for charitable purposes but applies business skills in order to expand the supporting organization's business scale, as well as to invest funds, time, and abilities to realize their social impact. Differing to investment in commercial enterprises, VP's characteristics lies in the way it considers its aims and returns, as well as its supporting methods.
Characteristics of VP:
| Support Provided (Funding/ Management) |
|
|---|
| Performance |
|
|---|
| Engagement Style |
|
|---|
Global Expansion of VP: Preceding Examples (US/Europe)
US
New Profit

Summary
Founded in 1999 in Boston, currently has 50 employees and an annual budget of $20M. The Monitor Group provides support in the form of both funding and human resources.Has provided financial and managerial support to a total of 40 NPOs. Target organizations show an annual average growth rate of 40%, and the cumulative number of beneficiaries exceeds two million people.
Principal Investees
Focuses on the area of education to investigate and select its target organization to invest in. Has supported "Teach for All" since its start.Social Venture Partners

Summary
Established in Seattle in 1997, 25 partner locations in the US, 2,500 members.Has provided financial and professional managerial support to a total of 300 NPOs. SVP Tokyo is active in Japan.
Principal Investees
Community-based action: all partner locations carry out their own investigation processes to select and support organizations that solve issues within the community.Europe
Impetus Trust

Summary
Established in London in 2002, approximately 20 employees. Cumulative investment of $6M until present.Has provided financial and long-term managerial support to a total of 13 NPOs. CVC and Apax are among its targets.
Principal Investees
Initially supported NPOs over a wide range of sectors, currently focused on solving poverty issues and social rehabilitation of former convicts.Noaber Foundation

Summary
Established in Dutch in 2000 by the founder of software company.Has invested over €1M in NPOs and social enterprises as impact investment. Investment period is up to 15 years.
Principal Investees
Focuses on the area of Health-care. Has provided financial and managerial support to a total of .54.NPOs.and 500 social enterprises.
Globalization of Venture Philanthropy: Asia
The venture philanthropy movement which spread in Europe and US in the ‘90s reached Asia in the late 2000s. They vary in size and reach but below are a list of major funds that adopt the methods of venture philanthropy.
- Fuping Development Institute (Beijing, China)
- Non-Profit Partners (Beijing, China)
- D3 Jubilee (Seoul, Korea)
- Sopoong Ventures (Seoul, Korea)
- Seed:s (Seoul, Korea)
- Social Venture Partners Tokyo (Tokyo, Japan)
- ECSEL (Shanghai, China)
- Non-Profit Incubator (Shanghai, China)
- Flow Inc. (Taipei, Taiwan)
- Social Ventures Hong Kong (Hong Kong, China)
- Sow Asia Foundation (Hong Kong, China)
- Center for Social Initiatives Promotion (Hanoi, Vietnam)
- Change Fusion (Bangkok, Thailand)
- Grassroots Business Development Fund(US/Thailand)
 Asian Venture Philanthropy Network(HO: Singapore)
Asian Venture Philanthropy Network(HO: Singapore)
Need for Private Sector-Led Support for Social Purpose Organizations
Structure of social issues and the importance of social purpose organizations
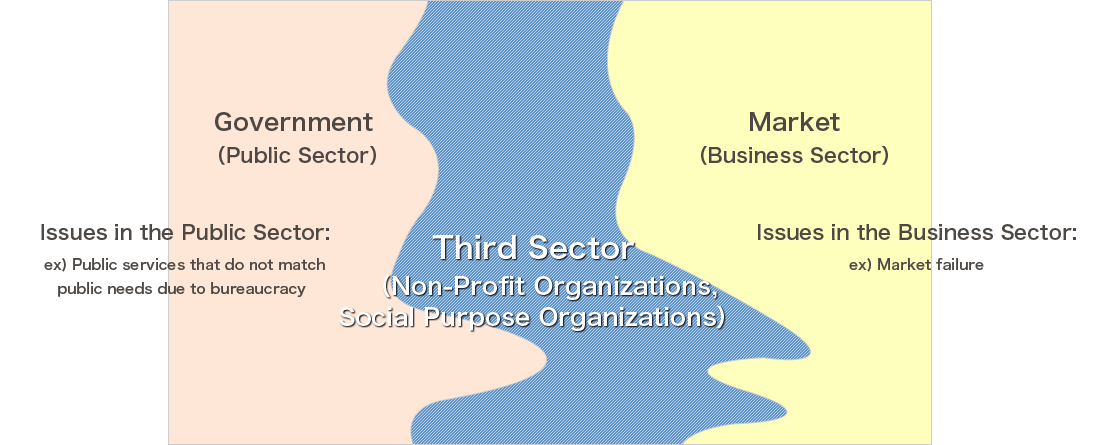
In answer to the social issues that arise due to the public and business sectors failing to address them, a third sector, which is constituted of non-profit organizations and social purpose organizations is needed to create new social frameworks and new values in order to address these social needs.
In order to support the initiatives in dealing with the new social needs, it is necessary to provide support towards social purpose organizations through the application of business management and investment experiences in the private sector.
Maximization of Social Impact
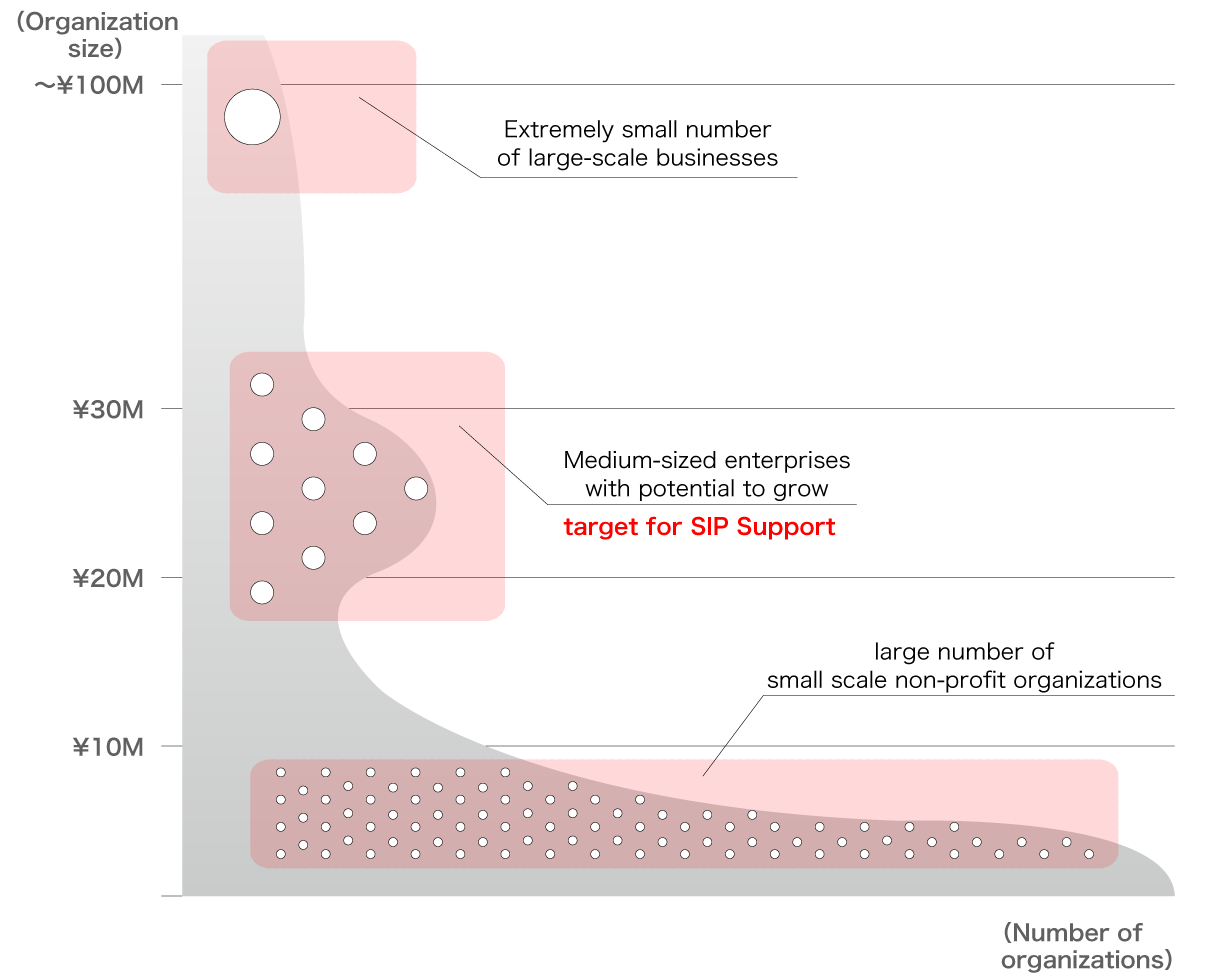
〔Distribution of the business scale and quantity of Social Purpose Organizations in Japan〕
- Organizational growth and social impact can be achieved by providing financial support and resources to non-profit organizations and social purpose organizations that have high potential for growth.
- The existing 40,000 non-profit organizations including social purpose organizations in Japan are constituted of a large number of small scale businesses.
- 64% of the existing non-profit (social purpose) organizations have an average of 1.4 employees and are under ¥5M in business volume, facing many challenges in terms of scale and efficiency.
- SIP selects non-profit organizations and social purpose organizations that have the potential to grow along with outstanding business models, and provides them with intensive support.
Issues behind Existing Supporting Organizations
- Organizations that support social purpose organizations at the start-up stage have often served to develop and incubate new entrepreneurs
- Private sector foundations provide support on a single-year basis and the use of funds is restricted. They do not hold the function in providing managerial support and mainly focus on monitoring the support receiving organization via financial account auditing.
- Support that combines financial capacity with professional expertise is seen as a necessary agent for the acceleration of the infrastructural development and business growth of the support receiving organization.
Non-Profit Support Organizations |
Private Sector Foundations |
JVPF |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets of Support | Mostly start-ups or early stage ventures |
Many groups targeted through open application, at any stage of business |
Mostly developing or expansion stage Work actively to identify projects, strictly performed selection process |
| Amount of Funding | About ¥1M per project |
Some projects receive several million yen, but use of funds is restricted and not used for general administrations |
¥10M in scale, mid-long term funding for business growth without restriction on usage Intensive management support by professionals & consultants with experience in business, venture capital, and private equity |
| Management Support | Mentoring during off-duty hours by young professional volunteers |
Mostly single-year support which provides very little management support |
Management support by experienced business people Pro-bono support (strategic consulting, law firm) Mid-long term support over 3-5 years |
| Social Impact | Mainly targets developing entrepreneurs |
Wide range support |
Maximize impact based on KPI and social impact indicators that SIP/support receiving organization define together |
| Governance | Board of directors |
Outcome is not emphasized, grantee is generally monitored via financial account auditing of fund use |
Result-oriented governance Board of directors |